A few years ago, artificial intelligence (AI) was synonymous with smart chatbots, recommendation engines, and image recognition. In 2025, the story is different. AI is moving into more autonomous decision-making, operating across data types and environments, and becoming embedded in real-world systems. According to PwC, nearly half of technology leaders in the October 2024 Pulse Survey said AI is fully integrated into their core business strategy. Global markets for AI-driven hardware, software, and services are showing double-digit growth almost everywhere.
If you want to build a global career in the technological industry, understanding this shift matters. Not just because ‘AI jobs’ may increase, but because the shape and intention of those jobs are changing. The kinds of tools you learn, the way you apply them, and the global contexts you work in are all evolving, and you need to evolve with them.
This begins with exploring five emerging AI technologies and understanding their real-world applications to prepare for a global pathway to the future of AI.
Exploring Top Five Emerging Technologies
Artificial intelligence is no longer a single discipline or tool. It is an ecosystem of rapidly evolving technologies. Each technology is bringing forth new ways of thinking, creating, and working. In 2025, the field is fragmenting and accelerating at the same time. While one branch is mastering creativity, another is focusing on autonomy, AI ethics, or real-time intelligence at the edge. Understanding these shifts will help you see how each technology complements the others, and how together, they redefine what 'intelligence' means.
1. Generative AI
Generative AI refers to systems capable of creating new content, such as text, images, audio, or even code, rather than simply analyzing existing data. It has become mainstream and is now the baseline for many AI-powered workflows.
- Enables creation of marketing copy, design prototypes, code snippets, and more with less manual effort.
- Large language models (LLMs) and image-generation tools are driving demand across creative, technical, and business roles.
- As these tools mature, the challenge shifts from 'how to generate' to 'how to supervise, refine, and integrate' the output into real processes.
2. Agentic AI
Agentic AI describes systems that do not just respond to prompts but plan, act, and adapt with minimal human supervision.
- These systems acquire goals, break them into tasks, and coordinate tools, data, and actions.
- Businesses are already using agentic AI to improve productivity, but they also face risks. Gartner predicts that over 40% of agentic AI projects may be cancelled by 2027 due to unclear business value.
- For you, this means learning to design, manage, and evaluate autonomous systems becomes as important as the underlying algorithms.
3. Multimodal AI
Multimodal AI is the capability of AI systems to handle many types of input or output, such as text, image, audio, and video, and fuse them for richer understanding.
- The next wave of AI is shifting from 'text only' models to ones that see, hear, and interpret multiple data streams simultaneously.
- A model may receive an image and spoken instruction, then generate a video summary or assembly instruction.
- In practical terms, professionals will need to know how to design and apply such systems, as well as how to deal with data fusion, multimodal training, and evaluation.
4. Explainable AI (XAI)
As AI becomes embedded in mission-critical systems (healthcare, finance, and governance), understanding how and why the AI made a decision is vital. Explainable AI (often called XAI) addresses this need.
- XAI gives users (and regulators) visibility into model decisions, enabling trust, accountability, and auditability.
- With new regulations, transparency and fairness are no longer optional.
- For you, mastering XAI means not only building powerful models but also building responsible, ethical, and traceable ones.
5. Edge AI
Edge AI refers to deploying AI models directly on devices or near the data source (rather than only in central clouds). It supports real-time decision-making, low latency, higher privacy, and lower bandwidth demands.
- The global edge AI market was estimated at USD 20.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow substantially.
- AI professionals are expected to work not just in 'the cloud' but on embedded devices, IoT systems, wearables, and distributed sensors.
- Skills in hardware-software integration, optimization, low-power models, and on-device inference will increasingly matter.
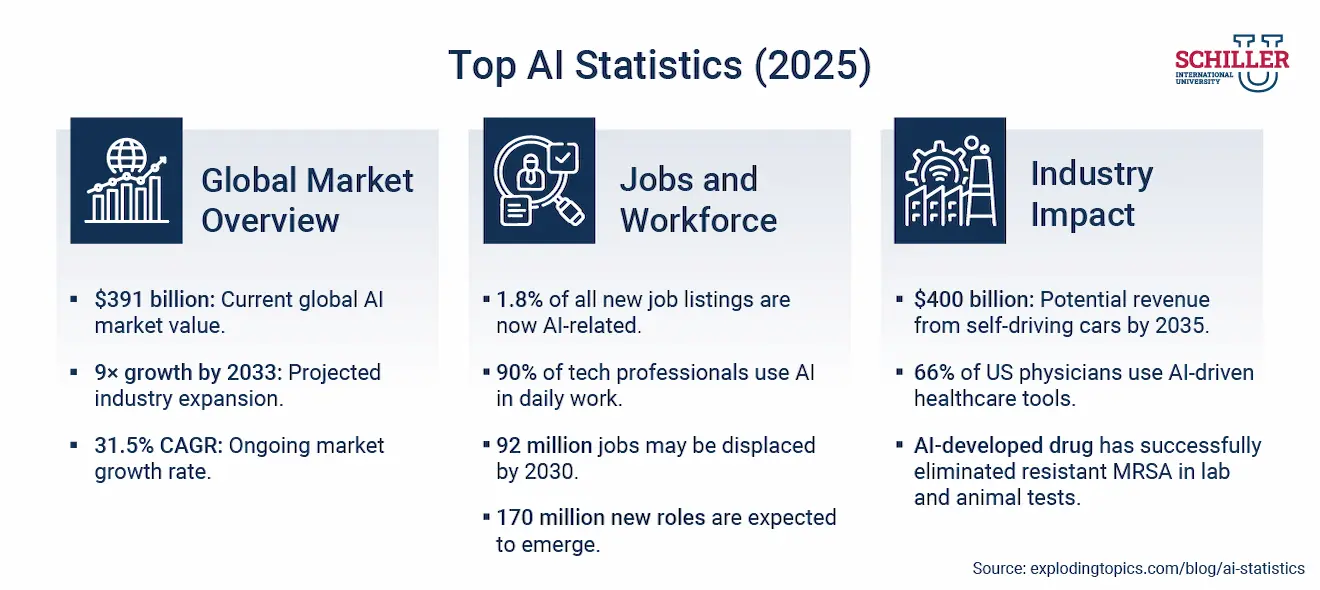
Real World Applications of AI in Industry
Emerging AI technologies converge, overlap, and reshape the systems we already rely on. What was once 'AI for automation' is now AI woven into decision-making, diagnostics, design, and defense. In 2025, the question is not where AI will be applied but how deeply it will integrate into everyday operations across industries. From hospitals to cybersecurity labs, these technologies are moving from prototypes to production, creating new professional roles that blend technical fluency with real-world judgment.
AI in Healthcare
Imagine systems that assist diagnosis by analyzing images, patient records, speech, and sensor data (multimodal), with agents that schedule follow-up, explain their decisions (XAI), and deploy on local devices (edge AI). Emerging AI technologies are already fundamentally changing care delivery, and they will create new roles in AI clinical informatics, AI ethics in healthcare, and edge device deployment for remote medicine.
AI in Cybersecurity
Cyber threats evolve fast. Generative AI helps craft phishing simulations and create synthetic data for training. Agentic AI monitors and autonomously responds to threats. Edge AI enables detection and response locally. Explainable AI ensures that the 'why' behind alerts is clear to human analysts. Roles will center on secure AI systems, autonomous defense, adversarial-AI modelling, and governance.
Intelligent Process Automation
Across industries, routine workflows are being automated, but the next step is for smarter, agentic AI to make decisions, generative AI to draft documents, multimodal AI to process diverse inputs, edge AI to perform local tasks, and XAI to provide oversight. International students prepared in applied AI can step into roles such as AI business analyst, AI workflow architect, or automation strategist.
Shadow AI
Shadow AI refers to AI that is developed or used informally within an organization, without oversight or governance. As emerging AI technologies become more accessible, the risk rises. Understanding where shadow AI arises, how to govern it, and how to detect it (through XAI, monitoring) is a key future job area. Skills here will include policy, ethics, audit, and embedding safe-AI practices in global teams.
Prepare for the Future of AI with Schiller
If you want to build the skills to succeed in this changing AI reality, Schiller International University's BSc in Applied Mathematics & Artificial Intelligence program offers exactly what you need. The comprehensive modules focus on hands-on learning in applied AI, not just theory.
- Applied learning focus: Rather than just theories of algorithms, you will work on real-world tasks, generative models, autonomous agents, multimodal systems, edge-AI deployment, and explaining AI outputs.
- Cross-campus study options: You can study in Germany, Spain, France, or the US, which will allow you to gain global exposure, diverse cultural insights, and an international network.
- Job-readiness for AI markets: The program is structured around the future of artificial intelligence demands, including roles emerging in 2026 and beyond. You will build a portfolio of applied projects, gain exposure to industry tools, and understand applied implementation.
By the time you graduate, you will know what the emerging AI technologies are and have built experience working with them. You will have understood how they fit into global industries and be ready to step confidently into jobs where you make a difference.
Emerging AI technologies are shaping the future of artificial intelligence and creating new career pathways. What matters now is to prepare, gain the skills for AI future jobs, position yourself for AI-powered innovation, and choose a study route that gives you real applied exposure, global mobility, and a supportive community. With the right focus, you will move from ‘interested in AI’ to ‘ready for the next wave of AI’.
The future does not wait. Start your next step by exploring Schiller’s BSc in Applied Mathematics and AI program to study in Europe or the US.
FAQs
Q1. Which AI technologies will create the most jobs in the future?
Answer: Roles tied to agentic AI (autonomous systems), edge AI (on-device intelligence), and multimodal AI (integrating diverse data types) are expected to grow rapidly. At the same time, explainable AI opens roles in ethics, audit, and governance, while generative AI continues to expand creative and technical functions.
Q2. Do I need a technical background to study AI?
Answer: A strong mathematical foundation and comfort with quantitative thinking will help, but many applied AI degrees (such as the one at Schiller) are designed for international students from diverse backgrounds, with support and pathways for those returning to study or changing career.
Q3. Are there English-taught AI degrees in Europe?
Answer: Yes. Many universities and institutions in Germany, Spain, and France now offer English-taught bachelor’s or master’s programs in artificial intelligence or applied mathematics with AI specializations. The Schiller BSc in Applied Mathematics & Artificial Intelligence is one such option with cross-campus flexibility.
Q4. Why is studying AI abroad beneficial for international students?
Answer: Studying abroad gives exposure to diverse cultures, networks, and industries, enhances language and intercultural skills, and provides access to global AI research and job markets. It also shows employers that you can adapt, relocate, and work in international teams.
Q5. Does Schiller International University offer training in applied AI?
Answer: Yes. Our applied mathematics and AI program emphasises applied learning. You will work on real-world tasks and gain industry-relevant skills in emerging AI technologies.

 Request information
Request information









